What is MongoDB?
MongoDB is a NoSQL (Not Only SQL), document-oriented database management system designed for ease of development and scalability. Unlike traditional relational databases, MongoDB stores data in flexible, JSON-like documents, making it ideal for handling unstructured or semi-structured data. Developed by MongoDB Inc., In the realm of database management, MongoDB stands as a powerhouse, revolutionizing the way organizations handle and process their data. With its flexible document-oriented structure and scalable architecture, MongoDB has become a go-to choice for businesses of all sizes.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deep into MongoDB, exploring its key features, benefits, differences between MongoDB and other data management systems, and the reasons why it’s reshaping the landscape of modern database management.
Key Differences between the MongoDB and Other Data Management System
MongoDB and relational database management systems (RDBMS) represent two distinct approaches to storing and managing data. While both serve the purpose of storing and retrieving data, they differ significantly in their architecture, data model, and use cases. Explore the significant differences between MongoDB and relational database management systems, aiding in choosing the optimal solution for your project needs.
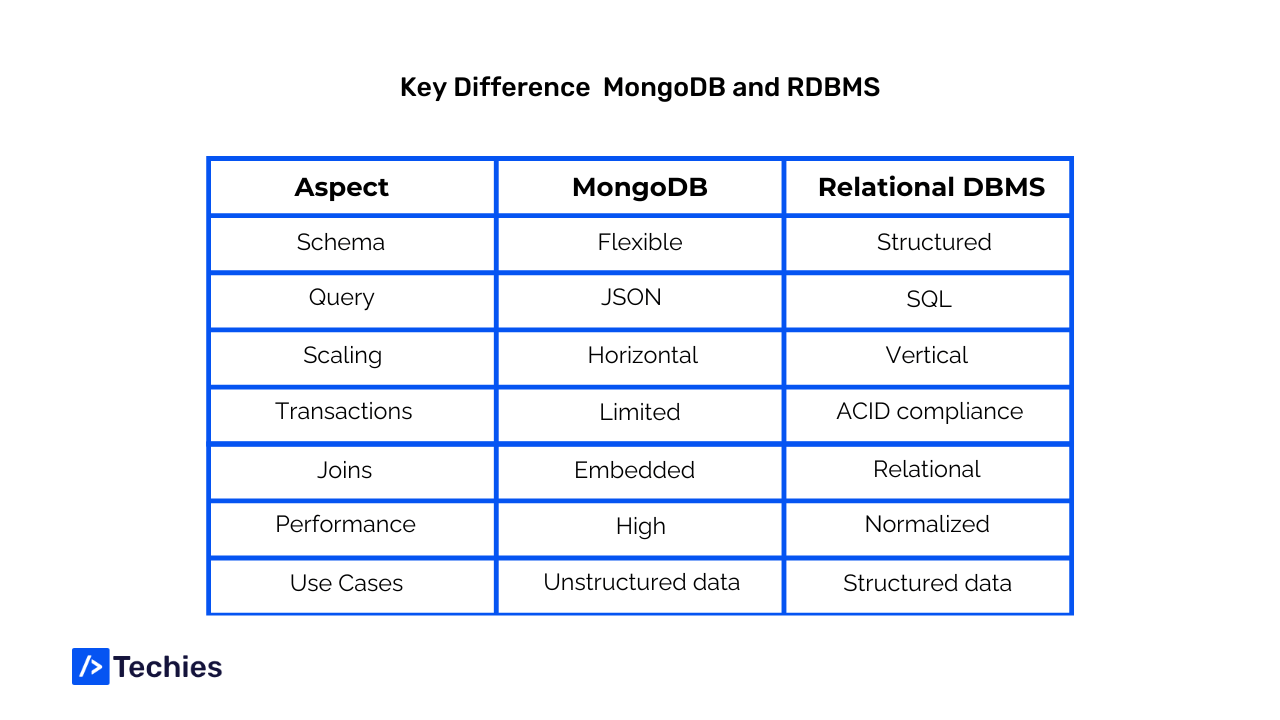
Data Model
MongoDB: MongoDB is a document-oriented NoSQL database. It stores data in flexible, JSON-like documents, allowing for nested data structures and dynamic schemas. Each document can vary in structure, providing greater flexibility for evolving data models.
Relational Database Management Systems: RDBMS, such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle, use a tabular data model with predefined schemas. Data is structured into tables, with each row representing a record and columns denoting attributes.RDBMS enforces a fixed schema, requiring all records within a table to adhere to the defined structure.
Scalability
MongoDB: MongoDB is designed for horizontal scalability. It employs sharding to distribute data across multiple nodes, enabling seamless scaling as data volumes and application demands increase. This distributed architecture makes MongoDB well-suited for handling large-scale applications and high-throughput workloads.
Relational Database Management Systems: While RDBMS also support scaling, they typically rely on vertical scaling by upgrading hardware resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage. Vertical scaling has limitations, making it challenging to scale seamlessly for rapidly growing datasets or high-concurrency scenarios.
Query Language and Transactions
MongoDB: MongoDB uses a query language inspired by JavaScript called the MongoDB Query Language (MQL). It provides powerful querying capabilities, including support for complex queries, aggregations, and geospatial queries. MongoDB also supports atomic operations on a single document.
Relational Database Management Systems: RDBMS uses SQL (Structured Query Language) for data manipulation and querying. SQL offers a standardized syntax for interacting with relational databases, supporting a wide range of operations such as joins, subqueries, and transactions spanning multiple tables.
ACID Compliance and Transactions
MongoDB: MongoDB sacrifices strict ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) compliance in favor of scalability and performance. It provides strong consistency guarantees within a single document but lacks support for multi-document transactions across multiple collections or databases.
Relational Database Management Systems: RDBMS adhere to the principles of ACID, ensuring data integrity, consistency, and transactional reliability. They support multi-document transactions, allowing for complex operations that span multiple tables while maintaining data consistency.
Use Cases
MongoDB: MongoDB is well-suited for applications requiring flexible schemas, real-time analytics, high scalability, and fast iteration. It excels in use cases such as content management systems, e-commerce platforms, and real-time analytics applications.
Relational Database Management Systems: RDBMS is ideal for applications with structured data, complex transactions, and strict data integrity requirements. They are commonly used in traditional enterprise applications, financial systems, and applications with well-defined relationships between entities.
Evolution of MongoDB
Structured Query Language (SQL) predates the World Wide Web. However, as websites became more complex, developers sought ways to generate content without the need to redeploy code dynamically. This led to the development of Not only SQL (NoSQL). NoSQL databases offer relaxed ACID (atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) properties, providing better performance, scalability, flexibility, and reduced complexity.
MongoDB was launched on August 27th, 2009. The initial release, Version 1, was basic. Version 2 introduced significant enhancements such as sharding, special indices, geospatial features, and improvements in memory and concurrency. Version 3 introduced the aggregation framework, serving as a modern alternative to the aging MapReduce framework.
Top Reasons to Choose MongoDB
Flexible Data Model
Scalability
High Performance
Rich Querying Capabilities
Community and Support
Integration with Modern Technologies
Overall, MongoDB’s flexibility, scalability, performance, rich querying capabilities, fault tolerance, community support, and integration capabilities make it a top choice for businesses and developers seeking a modern and versatile database solution.
Salient Features of MongoDB

Versatile Database Solution
Dynamic Schema Design
Scalability and Load Balancing
Aggregation Framework
Seamless Replication
Robust Security Measures
Native JSON Support
Efficient MapReduce Functionality
Conclusion
In conclusion, MongoDB emerges as a powerful and versatile database solution that offers a myriad of benefits over traditional relational database management systems. Its flexible document-oriented data model, horizontal scalability, high performance, rich querying capabilities, and strong community support make it an ideal choice for modern application development.
At DTechies, we understand the importance of selecting the right database management system for your project. Our team of experienced professionals is here to guide you through the decision-making process, providing expert advice and assistance tailored to your specific requirements.
Ready to harness the power of MongoDB for your next project?
Contact DTechies today for expert guidance and support!
FAQ's
What makes MongoDB different from traditional relational databases?
MongoDB differs from traditional relational databases in several key aspects. Firstly, MongoDB is a NoSQL database, meaning it doesn't rely on the tabular structure of relational databases. Instead, MongoDB stores data in flexible, JSON-like documents, allowing for dynamic schemas and nested data structures. Additionally, MongoDB is designed for horizontal scalability, while traditional relational databases often rely on vertical scaling. MongoDB also offers rich querying capabilities using the MongoDB Query Language (MQL), whereas relational databases use SQL. Overall, MongoDB provides greater flexibility, scalability, and performance for certain use cases compared to traditional relational databases.
Can MongoDB handle large volumes of data and high concurrency levels?
Yes, MongoDB is designed to handle large volumes of data and high concurrency levels efficiently. MongoDB employs sharding to distribute data across multiple nodes, enabling seamless horizontal scalability. This distributed architecture allows MongoDB to support massive datasets and handle concurrent read and write operations with ease.
How does MongoDB ensure data consistency and reliability?
MongoDB ensures data consistency and reliability through various mechanisms. Firstly, MongoDB supports replica sets, which maintain multiple copies of data across different servers. Replica sets provide fault tolerance and automatic failover, ensuring data availability and reliability in the event of node failures.
What kind of applications are best suited for MongoDB?
MongoDB is well-suited for a wide range of applications, particularly those with flexible data requirements, real-time analytics, and high scalability needs. It is commonly used in CMS, e-commerce platforms, mobile applications, IoT (Internet of Things) systems, and real-time analytics applications. MongoDB's flexibility, scalability, and performance make it an excellent choice for modern, data-driven applications that require agility and scalability.

ABOUT AUTHOR
Roopesh Jain
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Let's Work Together
Office Location
1042, Second Floor, Sector-4, Hiran Magri, Udaipur, Rajasthan - 313002
